Text · Screen Settings
Text · Screen Settings
View Mode Settings
page title
KRDS guides government officials who operate and manage digital government services on how to apply the guidelines according to the project’s context and objectives. It also provides reference materials for verifying the results of guideline application and reviewing implementation outcomes.
Page Contents
Priority of Application
From the User Experience Perspective
Among the guideline components, the Service Patterns' usability guidelines are divided into three levels of application based on their importance and user satisfaction from the
user’s perspective. To enhance the user experience for core services, the minimum requirement is to comply with the essential level, the lowest level of application.
When reviewing the levels of application, note that meeting a higher level does not guarantee compliance with the lower levels. Most top-level guidelines are intended to be
effective only after the lower-level guidelines have been met.
From the Step-by-Step Application Perspective
When applying the guidelines progressively, according to the service's and the operating institution's circumstances and objectives, refer to the step-by-step application elements defined by relevance, frequency of use, and feasibility.
Methods of Application by Context
Improving UI and UX Across the Service
1. Planning
In the planning stage, where the goals for a digital government service are established and the project is initiated, it is essential to define the scope of UI and UX tasks from the user’s perspective. By using these guidelines, you can define the UI and UX implementation goals and scope for the service and specify user experience quality requirements in concrete terms.
| Category | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Project Planning |
|
| Procurement |
|
2. Development
These guidelines present UI and UX principles and detailed guidance for building or redesigning a digital government service. By referring to the relevant items during the series of processes that improve the service’s UI and UX, such as analysis, design, implementation, and testing, you can implement and review consistent user-centered experiences more efficiently.
| Category | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Analysis |
|
| Design |
|
| Implementation |
|
| Test |
|
3. Operation
A digital government service is not complete once it is built; it must continue to provide service experiences optimized for user needs. By applying these guidelines throughout the ongoing review and enhancement of the service's UI and UX, you can develop and strengthen a structured quality management plan for the user experience.
| Category | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Current-State Analysis and Review |
|
| Establishing an Operation Plan |
|
| Improvement and Enhancement |
|
Applying UI and UX Improvements to Specific Tasks and Elements
These guidelines are developed based on core tasks and common user interface elements encountered in digital government services. By understanding the different types and examples of each component and properly combining related elements, you can deliver a consistent user experience while considering the unique features of each service.
Improving UI and UX for Individual Elements
When only specific screens or elements need UI and UX enhancements rather than the entire service, refer to the relevant components and basic patterns for that task.
-
Example: Improving the UI and UX related to “Navigation” in a service
- Refer to the components in the “Navigation” category, such as main menus, side menus, in-content navigation, breadcrumbs, and pagination.
-
Example: Improving the UI and UX related to “Help” in a service
- 'Refer to the usability guidelines in the “Help” basic pattern, including guidance areas, placeholders, inline text, tooltips, contextual help, and help panels.
Improving UI and UX for Tasks Not Included in the Service Patterns
When improving UI and UX for tasks not included in the service patterns, refer to similar items in the service patterns' detailed journeys or to guidelines for the elements that make up the task.
-
Example: Designing the UI for service sign-up, reservations, etc.
- Refer to the relevant items in the “Application” service pattern guidelines for tasks related to these processes.
- Refer to the guidelines for input forms, help, confirmation, and errors in the basic patterns.
- When designing the detailed UI, consult the component guidelines that define the service pattern and basic patterns.
Improving UI and UX for Mobile Services
As these guidelines are developed based on the task journeys of digital government service users, it is crucial to fully understand the concepts and purposes of each component
guideline and apply them according to the user’s goals and context in any usage environment.
When mobile web or app services need to be optimized based on usage conditions, such as screen size or interaction methods, refer to the following to enhance the user experience.
| Category | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Principle | Understand and become familiar with the content and key methods related to “Principle 6, services that consider diverse user situations.” |
| Style | Refer to the guidelines for each screen size, including responsive layout grids for placement elements. |
| Components and Patterns | Refer to the mobile-related items in the structural, type-specific, and platform considerations for each component, as well as the usability and accessibility guidelines. |
| Mobile-App-Specific Components | Refer to the detailed content in 'Components > Navigation > Tab Bars and Components > Layout > Splash Screen'. |
| Standard Prototypes | Refer to the mobile screens of the standard prototypes for each service journey, including the identity areas such as the header and footer. |
Verification of Application Results
Service operators and personnel can independently verify compliance with the Digital Government Service UI/UX Guidelines using the internal verification checklist, detailed compliance criteria, and available tools.
Verification Procedure
-
1. Preparation
Select the guideline application criteria and the scope of items to be reviewed for the target service, and prepare the necessary verification environment.
-
2. Execution
Verify each target item using the internal verification checklist and detailed compliance criteria, and assess whether each item complies.
-
3. Reporting
Prepare a detailed verification report based on the checklist and summarize the results as “Compliant – Not Compliant – Not Applicable” to assess overall compliance.
-
4. UI/UX Quality Improvement
Based on the verification results, set improvement priorities and develop and implement improvement plans in accordance with the guidelines.
Checklist

- 1.Classification of Compliance Criteria:A classification into use cases, structure, usability guidelines, interaction guidelines, etc.
- 2.Original Guideline Text
- 3.Compliance Criteria:Criteria used to determine whether the guideline is met
- 4.Verification Result Checkboxes:Recording results according to the compliance criteria
Detailed Compliance Criteria

- 1.Detailed Compliance Criteria
- 2.Screen or element to be inspected:Specifies the target and any exceptions that must be checked to determine compliance with the guideline.
- 3.Inspection procedure/method:Specifies the step-by-step procedures and methods for checking compliance.
- 4.Non-compliance examples:Presents frequent cases of non-compliance to support understanding of compliance criteria.
- 5.Original text of the relevant guideline
Evaluating Application Outcomes
After applying the guidelines, continuous improvement is required through outcome evaluation based on various qualitative and quantitative methodologies, including user feedback from the actual service.
Outcome Evaluation Methods
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Checklist-Based Evaluation | Compare the implementation status and compliance levels before and after applying the guidelines using the developed internal verification checklist. |
| “User Feedback” Collection and Analysis | Collect direct user input by applying the “User Feedback” basic pattern to the relevant services and pages. |
| Web Analytics Data Analysis | Select analysis metrics for each service pattern and quantitatively analyze the performance before and after applying the guidelines. |
Outcome Evaluation Procedures
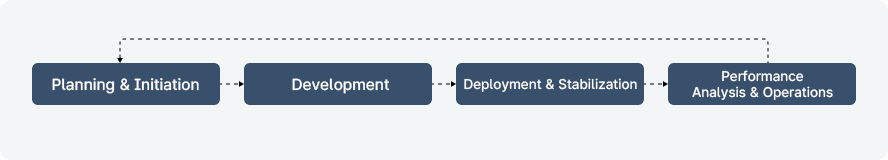
-
1. Planning and Procurement
This stage establishes the basis for performance evaluation by defining the scope and objectives of guideline application within the project and specifying the requirements for verifying the outcome of guideline application in the RFP.
-
2. Development
This stage involves securing pre-application data for the guideline application scope. If user feedback or web analytics data is unavailable, it is essential to collect such data during the development phase.
-
3. Deployment and Stabilization
This stage checks and reinforces the data collection approach after application. If the “User Feedback” pattern or web analytics code has been implemented, it is essential to verify during the stabilization period that data is being collected properly.
-
4. UI/UX Performance Analysis and Operations
This stage analyzes performance by comparing pre- and post-application data, and for areas where the effects are insufficient, identifies the causes and develops improvement measures. If an ongoing application occurs during service operation, continuous performance analysis is conducted through periodic evaluation and monitoring in accordance with the annual plan.